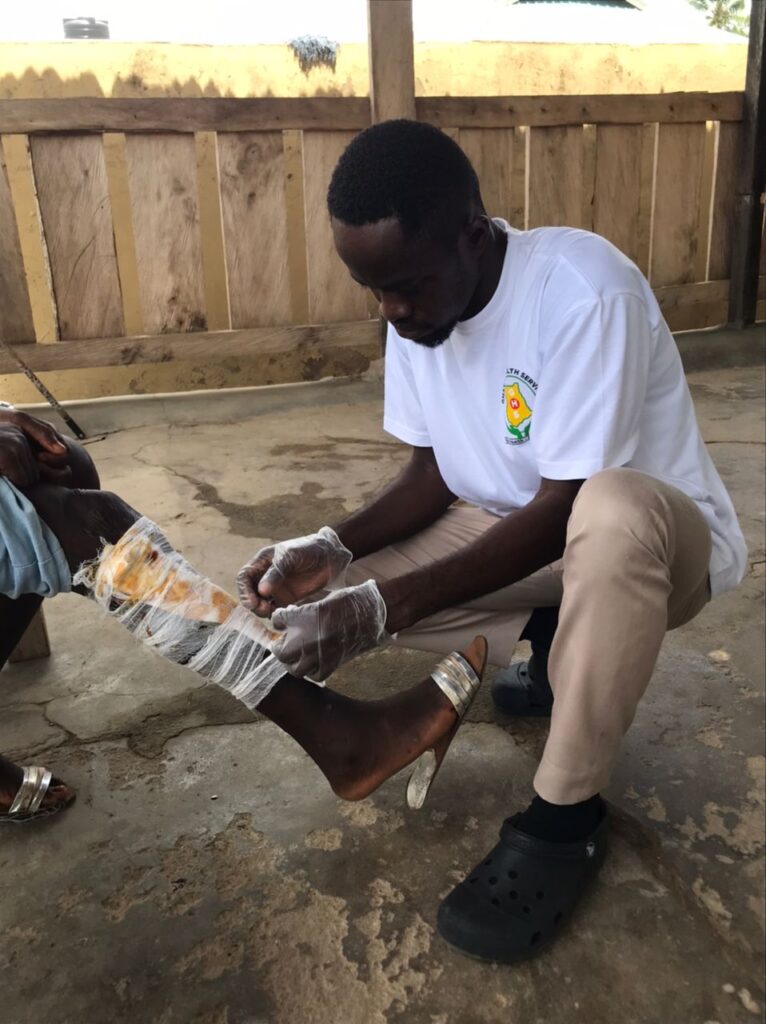
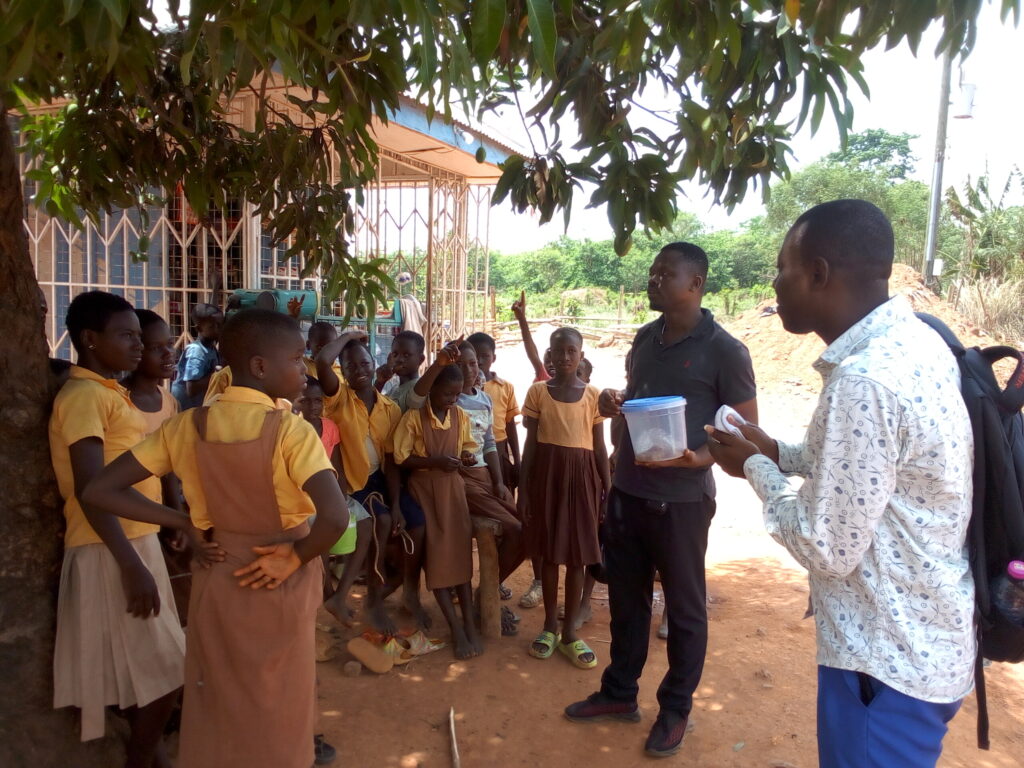
NTDs are treatable but, as neglected diseases, they are not seen as a priority.
Anesvad Foundation helps make the control and elimination of these neglected diseases a possibility.
What are Neglected Tropical Diseases?
Impoverished populations in rural areas of sub-Saharan Africa are affected by a set of infectious diseases known as Neglected Tropical Diseases (NTDs).
These diseases are not classified as neglected because they are untreatable, or because we do not know what actions to take to prevent them, but rather because they are overlooked. Factors such as poverty, exclusion, limited accessibility, etc., mean that the required treatment is not received.
Anesvad Foundation works in line with WHO guidelines, promoting the integration of control measures in endemic areas and strengthening intersectoral interventions. This enables us to better control transmission via pathogens such as parasites, bacteria, fungi, toxins and viruses.
What are Skin-Related Neglected Tropical Diseases?
The main Neglected Tropical Diseases (NTDs) typically cause skin alterations, leaving marks on those infected as a lifelong reminder of the disease.
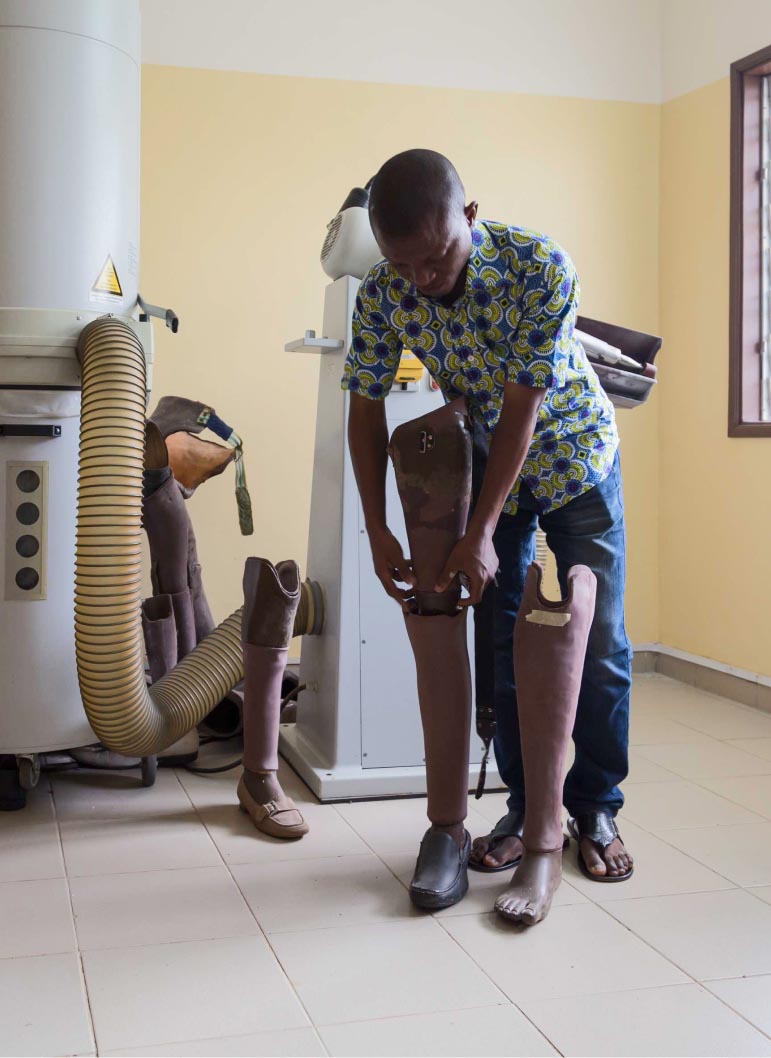
In countries such as Togo, Ghana, Benin and Côte d’Ivoire, having these marks, despite the fact that in many cases they are a sign of recovery, can lead to isolation and stigmatisation among the population. The diseases can lead to deformities, disabilities, mobility difficulties and other problems which may require surgery, or which may even end up being fatal if not treated in time.
Spotting cutaneous manifestations and early diagnosis and treatment is crucial if patients are to be fully cured and to avoid further disruption to internal organs or other systems.
Moreover, these marks and diseases are preventable at source because their transmission is influenced by, among other factors, limited access to public health services and safe water, sanitation and hygiene in affected communities. However, because they are neglected diseases, affecting neglected areas, communities, lives, etc., they are not treated as a priority when it comes to global health programmes and funding.
More than one billion people in 149 countries are affected by one of the 20 existing NTDs. This has led the World Health Organisation (WHO) to develop a roadmap which commits to reducing their incidence by 90% by 2030.
Buruli ulcer
- This debilitating disease is caused by the bacteria Mycobacterum ulcerans.
- Although its forms of transmission are unknown, it is related to stagnant and unsafe water.
- It is present in 33 tropical-climate countries and is mostly concentrated in Western and Central Africa.
- Most patients are children from Sub-Saharan Africa.
- Treatment and recovery require several weeks of medication and treating wounds. In severe cases, it requires skin grafting and surgery.
- Treating it with antibiotics is cheap and effective, but if it is not treated in time it can lead to problems of morbidity, stigma and disability.
Leprosy
- Leprosy is a chronic infectious disease caused by the bacteria Mycobacterium leprae.
- It is transmitted by prolonged contact with people who suffer from it.
- If not treated in time, it can cause progressive and permanent skin lesions, affect the nerves, the mucosa of the respiratory tract, and eyes.
- It can be cured through multi-drug therapy and once the treatment is under way, the people affected by leprosy no longer transmit it.
- The stigma associated with leprosy in developing countries remains one of the biggest hindrances to its detection and treatment.
Yaws
- This is an infectious and disfiguring disease caused by bacteria similar to the bacteria which causes syphilis.
- It is transmitted by direct contact, via small lesions, with an infected person.
- Between 75% and 80% of patients are children under 15. It affects the skin, bones and cartilage, causing disability if not treated in time.
- It can be cured with one oral dose of azithromycin, an antibiotic found in any chemist and costing no more than 4.50 euros.
- But for insufficient resources, it could be eradicated.
Lymphatic filariasis
- This is transmitted in parasites called nematodes (roundworms) carried by mosquitos.
- Currently, this disease is endemic in 73 countries.
- Filarial worms are reproduced in the lymphatic system and generate larvae that circulates around the blood of the infected person.
- It can cause hypertrophy in extremities, causing pain, serious disability and social stigma.
- Preventive chemotherapy is the most effective treatment to stop its spread.
Dracunculosis
- Also known as Guinea worm disease.
- Caused by a parasite, it is spread by means of stagnant water with infected fleas.
- Symptoms include painful blisters on the skin, fever and joint pain. It is a debilitating disease which can cause long-term disability.
- It is on the verge of eradication: 27 human cases were reported in 2020.
- There is no vaccine to prevent the disease and no drugs to treat it, but various preventive strategies based on water sanitation and hygiene have brought the disease to this point.
Leishmaniasis
- It is transmitted to humans via bites from mosquitoes and sandflies which carry the parasite.
- There are three main forms of leishmaniasis: cutaneous, mucocutaneous and visceral.
- It can cause long-term disability and disfigurement.
- It is estimated that there are between 700,000 and 1 million new cases each year. Drugs exist for its treatment and cure, but they are sometimes difficult to use.
Mycetoma, chromoblastomycosis and other deep mycoses
- A chronic, destructive bacterial or fungal disease of the skin, subcutaneous tissues and bones.
- Symptoms include an inflammatory mass on the skin, pain, ulceration and pus discharge.
- If left untreated, it can result in amputation or disability.
- Its global burden is unknown, but it is endemic in Africa, Latin America, Asia and Europe, especially in areas with short rainy seasons and long dry seasons which favour the growth of thorny shrubs.
- Treatment is lengthy, has multiple side effects, is expensive, is not available in endemic areas and, above all, is often unsatisfactory.
Onchocerciasis
- Also known as river blindness.
- Caused by a parasite transmitted via infected black flies.
- Symptoms include disfiguring skin conditions and blindness, which may be permanent.
- 99% of cases occur in 31 countries in sub-Saharan Africa.
- A 2017 study estimated that 14.6 million of those infected had skin damage and 1.15 million had suffered vision loss.
- The main strategy being applied is the mass administration of ivermectin, once a year, for a period of 10-15 years.
Scabies and other ectoparasites
- Scabies is a skin disease caused by a mite and transmitted from person to person via direct skin contact.
- Diseases associated with these parasites include pediculosis (lice infestation), tungiasis (flea infestation), and cutaneous myiasis (fly infestation).
- They can cause pain, secondary infections and other symptoms.
- Effective treatments are available, but they do not kill the larvae of the parasite.
- The number of people worldwide suffering from scabies is estimated at 200 million.
Schistosomiasis
- Also known as bilharzia.
- Caused by infection with worms and transmitted via contact with fresh water contaminated with the larvae of the parasite.
- Symptoms include itchy skin, abdominal pain and diarrhoea, and can cause long-term liver, kidney and lung damage.
- Schistosomiasis control focuses on reducing the number of cases through regular, large-scale, population-wide treatment which is effective, safe and low-cost. However, it is estimated that of the over 251.4 million people who would have needed treatment in 2021, only 75.3 million received it.
Other NTDs which are not skin-related:
- Chagas’ disease.
- Trachoma.
- Taeniasis and cysticercosis.
- Dengue and chikungunya.
- Echinococcosis.
- Trematodiasis.
- Human African trypanosomiasis.
- Snakebite poisoning.
- Rabies.
- Soil-transmitted helminthiases.
Our data from 2023
- Countries all around subsaharan Africa
- Almost 60,000 people are part of our community
- 84 operational projects
- + 25 partner organisations
- €7.7 million in direct investment